Qui aura 20 en maths ?
💯 Teste ton niveau de maths et tente de gagner un des lots !S'inscrire au jeu →
Nouveau
🔥 Découvre nos fiches d'exercices gratuites avec corrections en vidéo !Accéder aux fiches →
Lire des limites dans un tableau de variation - Exercice 4
5 min
10
Question 1
Soit le tableau de variation de la fonction ci-dessous :
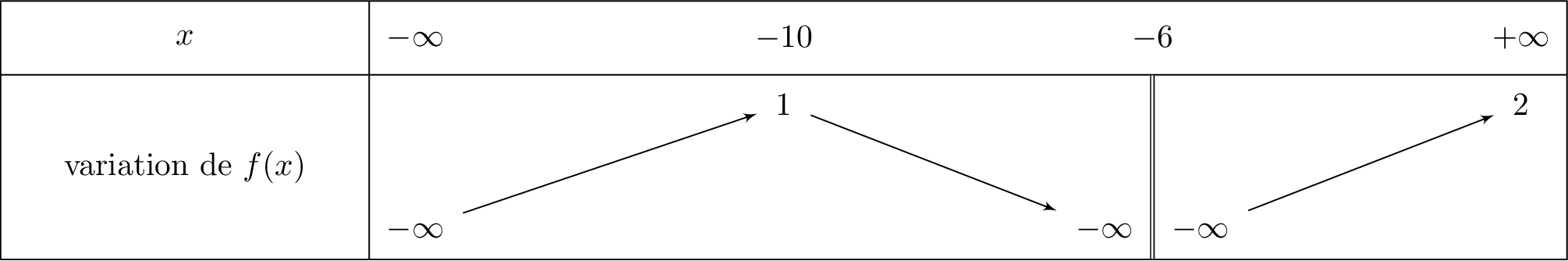

Quelle est l'ensemble de définition de de la fonction .
Correction
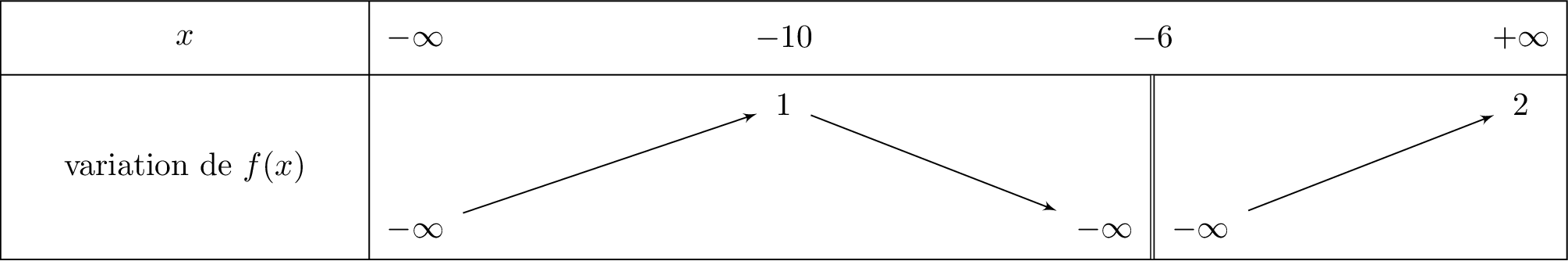
Le domaine de définition est alors :
Question 2
Quelles sont les limites de aux bornes de . Que peut-on en déduire graphiquement?
Correction
Si où est une valeur finie alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
Si où est une valeur finie alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
Si où est une valeur finie alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
Si alors la fonction admet une asymptote verticale d'équation
Si alors la fonction admet une asymptote verticale d'équation
Si alors la fonction admet une asymptote verticale d'équation
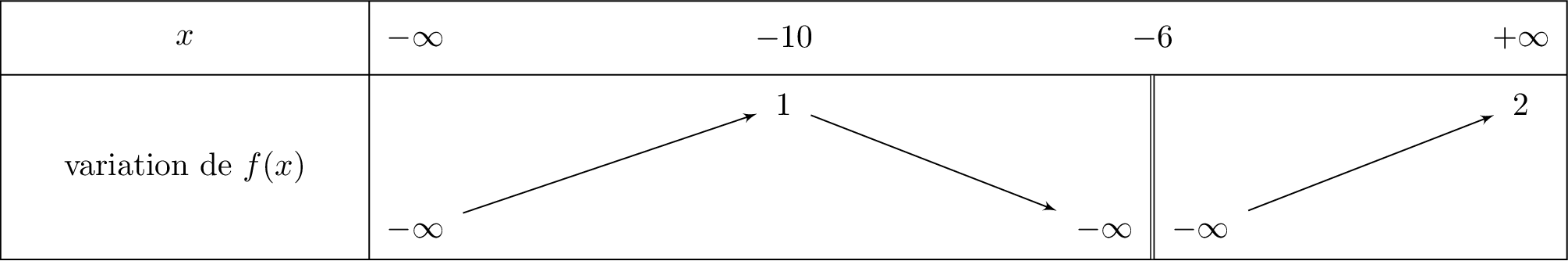
; ; et
Ainsi :
alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
alors la fonction admet une asymptote verticale d'équation
alors la fonction admet une asymptote verticale d'équation